MySQL Connector
MySQL is a Relational Database Management system (RDBMS) that consists of a multithreaded SQL server. It supports different back ends, several different client programs and libraries, administrative tools, and a wide range of application programming interfaces.
In the OvalEdge application, MySQL Connector allows users to crawl and profile the datasets such as Tables, Columns, Views, Procedures, and Synonyms and helps build the data catalog and lineage.
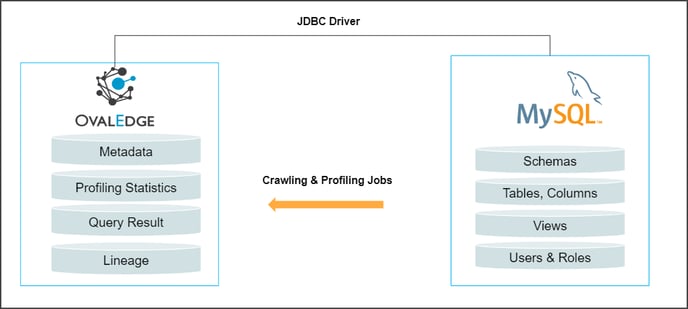
Connector Capabilities
The following is the list of objects and data types supported by the MySQL connector.
| Functionality | Supported Objects |
| Crawler |
Tables, Table Columns, Views, Stored Procedures, Supported Datatypes: int, tinyint, smallint, medium, bigint, float, double, decimal, date, datetime, timestamp, time, year, char, varchar |
| Profiler | Table Profiling: Row count, Columns count, and View sample data View Profiling: Row count, Columns count, View sample data Column Profiling: Min, Max, Null count, distinct, top 50 values Full Profiling |
| Query | Select, Insert, Update, Delete Joins outside database Aggregations Group By Order By |
| Lineage | Table lineage Column lineage |
Prerequisite
The following are the prerequisites required for establishing a connection between the connector and the OvalEdge application.
- Driver Details.
- Set up a Service account with the required permissions.
- Configure environment variables (Optional).
Driver Details
Driver: MySQL 8.0.25 is recommended for use with MySQL Server 8.0, 5.7, and 5.6. Please upgrade to MySQL Connector 8.0.25
|
Driver |
Version |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
JDBC |
8.0.25 |
https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java/5.1.29 |
Note: By default the service account provided for the connector will be used for any query operations. If the service account has to write privileges, then Insert/Update/Delete queries can be executed.
Service Account with Minimum Permissions
The following are the privileges required for a service account to crawl and profile the data.
| Operation | Minimum Access Permission |
| Connection Validation | Select and Usage |
| Crawling | Select and Usage |
| Profiling | Read |
| Query execution | Select |
Establish Environment Variables (Optional)
This section describes the settings or instructions that users should be aware of prior to establishing a connection. If your environments have been configured, skip this step.
Configure Environment Names
The Environment Names allow users to select the environment configured for the specific connector from the dropdown list in the Add Connector pop-up window.
You might want to consider crawling the same schema in both stage and production environments for consistency. The typical environments for crawling are PROD, STG, or Temporary, and may also include QA or other environments. Additionally, crawling a temporary environment can be useful for schema comparisons, which can later be deleted, especially during application upgrade assistance.
Steps to Configure the Environment
- Navigate to Administration > System Settings.
- Select the Connector tab.
- Find the Key name “connector.environment”.
- Enter the desired environment values (PROD, STG) in the value column.
- Click ✔ to save.
Establish a connection
To establish a MySQL connection,
- Log into the OvalEdge application
- In the left menu, click on the Administration module name, and click on the Connectors sub-module name. The Connectors Information page is displayed.
- Click on + New Connector. The Add Connector pop-up window is displayed.
- Select the connection type as MySQL. The Add Connector with MySQL-specific details are displayed.
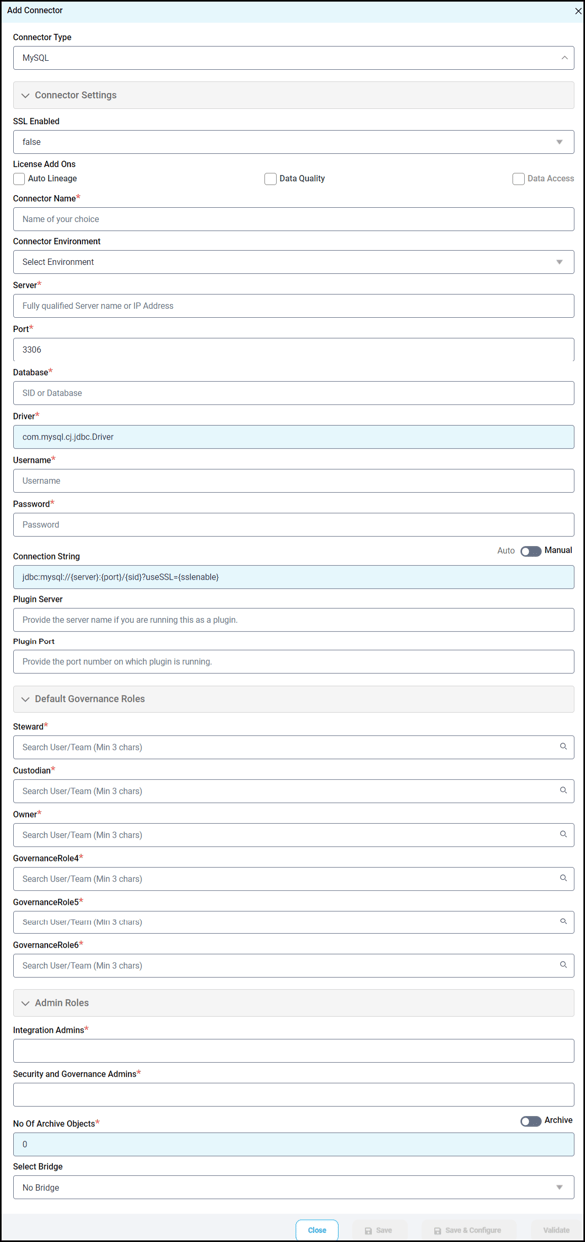
|
Fields |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Connector Type |
By default, the selected connection type is displayed as MySQL. If required, the connection type can be changed, and depending on the connector selected, fields are displayed accordingly. |
| Connector Settings | |
|
SSL Enabled |
SSL Enabled drop-down list allows you to select either true or false options. |
|
License Add Ons |
All the connectors will have a Base Connector License by default that allows you to crawl and profile to obtain the metadata and statistical information from a datasource. OvalEdge supports various License Add-Ons based on the connector’s functionality requirements.
|
|
Connector Name* |
Select a connection name for the MySQL database. Users can specify a reference name to identify the MySQL database connection in OvalEdge. Example: MysQL_Connection_DB1 |
|
Connector Environment |
The environment drop-down list allows you to select the environment configured for the connector from the drop-down list. For example, PROD, or STG (based on the configured items in the OvalEdge configuration for the connector.environment). |
|
Server* |
Specify the name of the MySQL database instance server URL, which is accessible by the OvalEdge application. Format: <account>.mysqlcomputing.com |
|
Port* |
By default, port number 3306, related to the MySQL database, is displayed. If needed, a new port number can be provided. |
|
Database* |
Provide the name of the database that is associated with the MySQL connection, if necessary. It is a user-specified database name to crawl the metadata of selected connectors. |
|
Driver* |
A JDBC driver is a Java library file with the extension .jar that connects to a database. The driver details associated with the MySQL database will be auto-populated by default. Example: net..client.jdbc.SQLDriver |
|
Username* |
Enter the Service Account Username for the MySQL Server name. |
|
Password* |
Enter the password for the MySQL Server name. |
|
Connection String |
Set the Connection string toggle button to automatic, to get the details automatically from the credentials provided. Alternatively, you can manually enter the string. Format: jdbc:MySql://{server}:3306/{sid} Example: jdbc:MySql://oval.cvbnxxcvvwcraues.us-east-2.MySql.amazonaws.com:3306;database=customers |
|
Plug-in Server |
Enter the server name if you are running this as a plugin. |
|
Plug-in Port |
The port number on which the plugin is running. |
|
Default Governance Roles |
|
|
Default Governance Roles* |
The admin will select a specific user or a team from the governance roles (Steward, Custodian, Owner) that get assigned to the data asset. The dropdown list displays all the configurable roles (single user or a team) as per the configurations made in the OvalEdge Security > Governance Roles. |
|
Admin Roles |
|
|
Admin Roles* |
Select the required admin roles for this connector.
|
|
No of archive objects* |
It is the number of last modifications made in the metadata data of a dataset at Remote/source. By default, the number of archive objects is set to disable mode. Click on the Archive toggle button and enter the number of objects wish to archive. For example, if a user updates the count as 4, the connection is crawled. It will provide the last 4 changes that occurred in the remote/source of the connector. You can observe these changes in the ‘version’ column of the ‘Metadata Changes’ module. |
|
Select Bridge |
With the OvalEdge Bridge component, any cloud-hosted server can connect with any on-premise or public cloud data sources without modifying firewall rules. A bridge provides real-time control that makes managing data movement between any source and destination easy. For more information, refer to Bridge Overview. When the bridge is configured and added, the Bridge ID will be displayed in the dropdown menu, or it will be displayed as "NO BRIDGE." For more information, refer to Bridge Overview |
5. After filling in all the connection details, select the appropriate button based on your preferences.
a. Validate: Click on the Validate button to verify the connection details. This ensures that the provided information is accurate and enables successful connection establishment.
b. Save: Click on the Save button to store the connection details. Once saved, the connection will be added to the Connectors home page for easy access.
c. Save & Configure: For certain Connectors that require additional configuration settings. Click on the Save & Configure button. This will open the Connection Settings pop-up window, allowing you to configure the necessary settings before saving the connection.
6. Once the connection is validated and saved, it will be displayed on the Connectors home page.
Note: * (asterisk) indicates the mandatory field required to create a connection. Once the connection is validated and saved, it will be displayed on the Connectors home page.
Note: You can either save the connection details first, or you can validate the connection first and then save it.
Connection Validation Details
|
S.No. |
Error Message(s) |
Description |
|
1 |
Failed to establish a connection, Please check the credentials |
Invalid User Name, and in case of the wrong password. |
Note: If you have any issues creating a connection, please contact your assigned OvalEdge Customer Success Management (CSM) team.
Connector Settings
Once the connection is established successfully, various settings are provided to fetch and analyze the information from the data source. The connection settings include Crawler, Profiler, Access Instruction, and Others.
|
Connector Settings |
Description |
|
Crawler |
Crawler settings are configured to connect to a data source and collect and catalog all the data elements in the form of metadata. Check out the crawler options to set the crawler's behavior in the Crawler & Profiler Settings. |
|
Profiler |
The process of gathering statistics and informative summaries about the connected data source(s). Statistics can help assess the quality of data sources before using them for analysis. Profiling is always optional; crawling can be run without profiling also. For more information, refer to Crawler & Profiler Settings |
|
Data Access |
The Data Access Authorization is included in the crawler-specific connector settings to ensure that the right user is accessing the query sheet and queries in the data catalog. Here the system validates the user credentials and allows that particular user to access the query sheet and queries in the data catalog. |
|
Access Instruction |
Access Instruction allows the data owner to instruct other users on using the objects in the application. |
|
Business Glossary |
The Business Glossary setting provides flexibility and control over how they view and manage term association within the context of a business glossary at the connector level. |
|
Others |
The Send Metadata Changes Notifications option is used to set the change notification about the metadata changes of the data objects.
|
Note: For more information, refer to the Connector Settings.
The Crawling of Schema(s)
You can use the Crawl/Profile option, which allows you to select the specific schemas for the following operations: crawl, profile, crawl & profile, or profile unprofiled. For any scheduled crawlers and profilers, the defined run date and time are displayed to set.- Navigate to the Connectors page, and click on the Crawl/Profile option.
- Select the required Schema(s).
- Click on the Run button that gathers all metadata from the connected source into OvalEdge Data Catalog.
Note: For more information on Scheduling, refer to Scheduling Connector
Copyright © 2023, OvalEdge LLC, Peachtree Corners GA USA